Appearance
the basic structure of PCB board
PCB serves as the carrier for electronic components and the provider of electrical connections. We can imagine it as the "foundation and road system" of a city.
Some Common Components
Components are the "inhabitants" and "functional units" on a PCBA.
3.1 Passive Components
Resistor
- Symbol:
-□- - Function: Limits current, divides voltage, shunts current. Unit is Ohm (Ω).
- Common Types: Carbon Film Resistor, Metal Film Resistor, Chip Resistor (SMD), Precision Resistor, Potentiometer (Variable Resistor).
- Symbol:
Capacitor
- Symbol:
-||-(Non-polarized),-|(-(Polarized, e.g., Electrolytic) - Function: Stores electrical charge, filters, couples/decouples signals, tunes circuits. Unit is Farad (F).
- Common Types: Ceramic Capacitor (MLCC, small size), Electrolytic Capacitor (Aluminum/Tantalum, high capacitance, polarized), Film Capacitor.
- Symbol:
Inductor
- Symbol:
-⏚⏚- - Function: Stores magnetic energy, blocks AC while allowing DC, filters. Unit is Henry (H).
- Common Types: Wire-wound Inductor, Chip Power Inductor (SMD), Ferrite Bead (suppresses high-frequency noise).
- Symbol:
3.2 Active Components
Diode
- Symbol:
-|>|-(Arrow indicates conventional current flow in forward bias) - Function: Unidirectional current flow. Used for rectification, voltage regulation, protection, and light emission (LED).
- Common Types: Rectifier Diode, Schottky Diode (high-speed), Zener Diode (voltage regulation), Light-Emitting Diode (LED).
- Symbol:
Transistor
- Function: Signal amplification, electronic switching. The core building block of modern electronics.
- Common Types:
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT):
NPN/PNP, commonly used for analog signal amplification and switching. - Field-Effect Transistor (FET / MOSFET): The fundamental unit of digital integrated circuits (e.g., CPUs, memory). Offers high switching speed and low drive power.
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT):
Integrated Circuit (IC)
- Symbol: Typically represented by a rectangle/box with the part number.
- Function: Miniaturizes an entire complex circuit (billions of transistors) into a single packaged chip to perform specific functions.
- Common Types:
- Microprocessor / Microcontroller: e.g., MCU, CPU. The "brain" of a system.
- Memory: e.g., RAM, ROM, Flash memory. Stores data and programs.
- Power Management ICs: e.g., LDO (Low-Dropout Regulator), DC-DC Converters. Manage and regulate power supply.
- Operational Amplifier (Op-amp): Used for analog signal amplification and processing.
- Logic Gates: Implement basic Boolean functions (AND, OR, NOT, etc.).
3.3 Other Important Components
- Connectors: Used for board-to-board or board-to-peripheral (e.g., power, USB) connections. Examples: Pin headers, Sockets, USB ports, RJ45 Ethernet jacks.
- Crystal Oscillator: Provides a precise clock signal, the "heartbeat" for timing in circuits.
- Sensors: Convert physical quantities (e.g., temperature, humidity, light, pressure) into electrical signals. Examples: Temperature sensor, Accelerometer.
- Relay: An electromechanical switch that uses a small current to control the switching of a much larger current.
Calculation
U=IR P=UI
The pcb board is drawn by using the Jialichuang platform
.png)
.png)
Design simple PCB board
SEKTCH OF PCB .png)
PCB ![PCB].png)
2D PCB BOARD 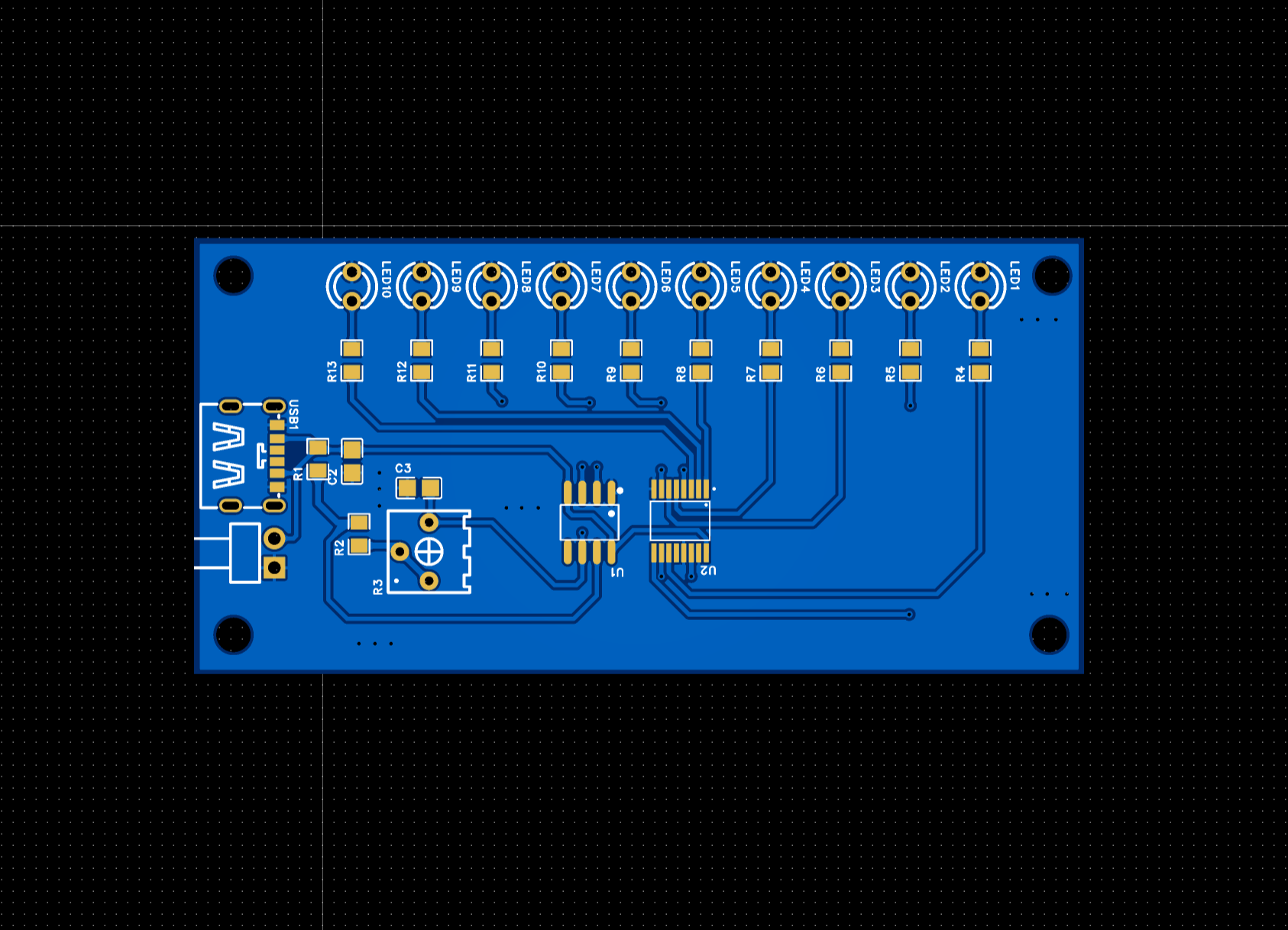
3D PCB BOARD .png)
Physical pcb (1).jpg)