CAD design
1. Build design project and build new component
Get ready and join the team.
2. Design your first 3D model
Process
Make the base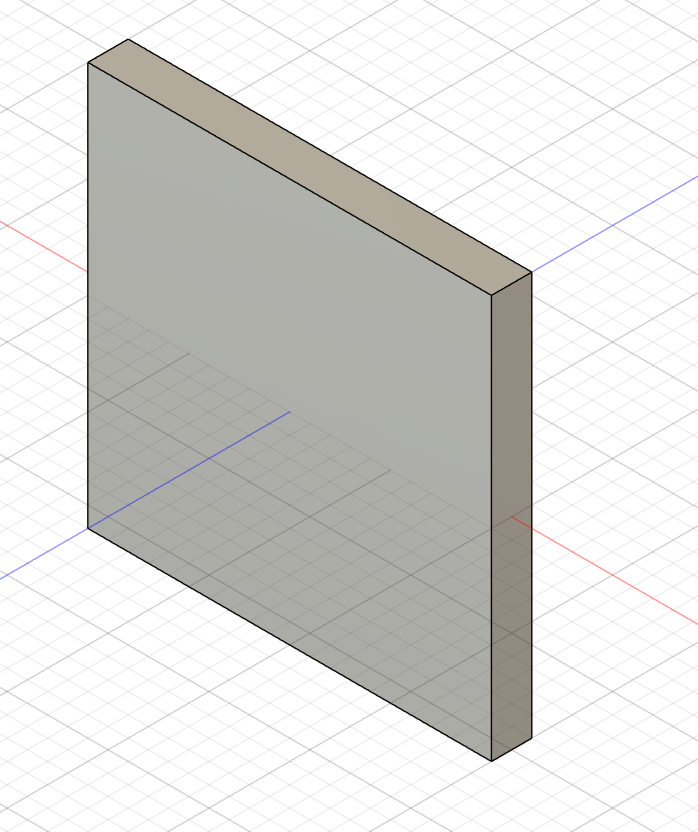
Make a shelf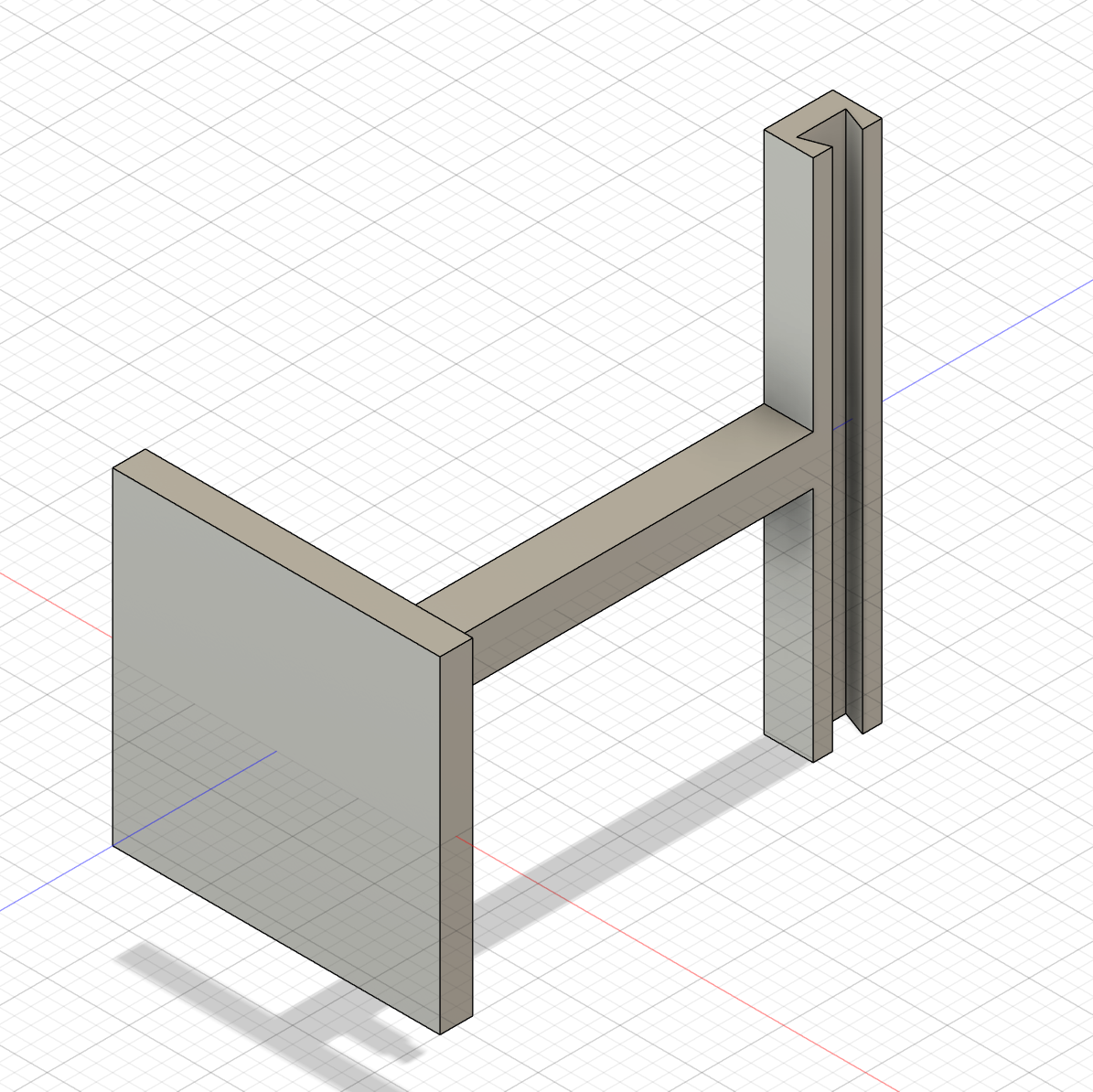
Make the slider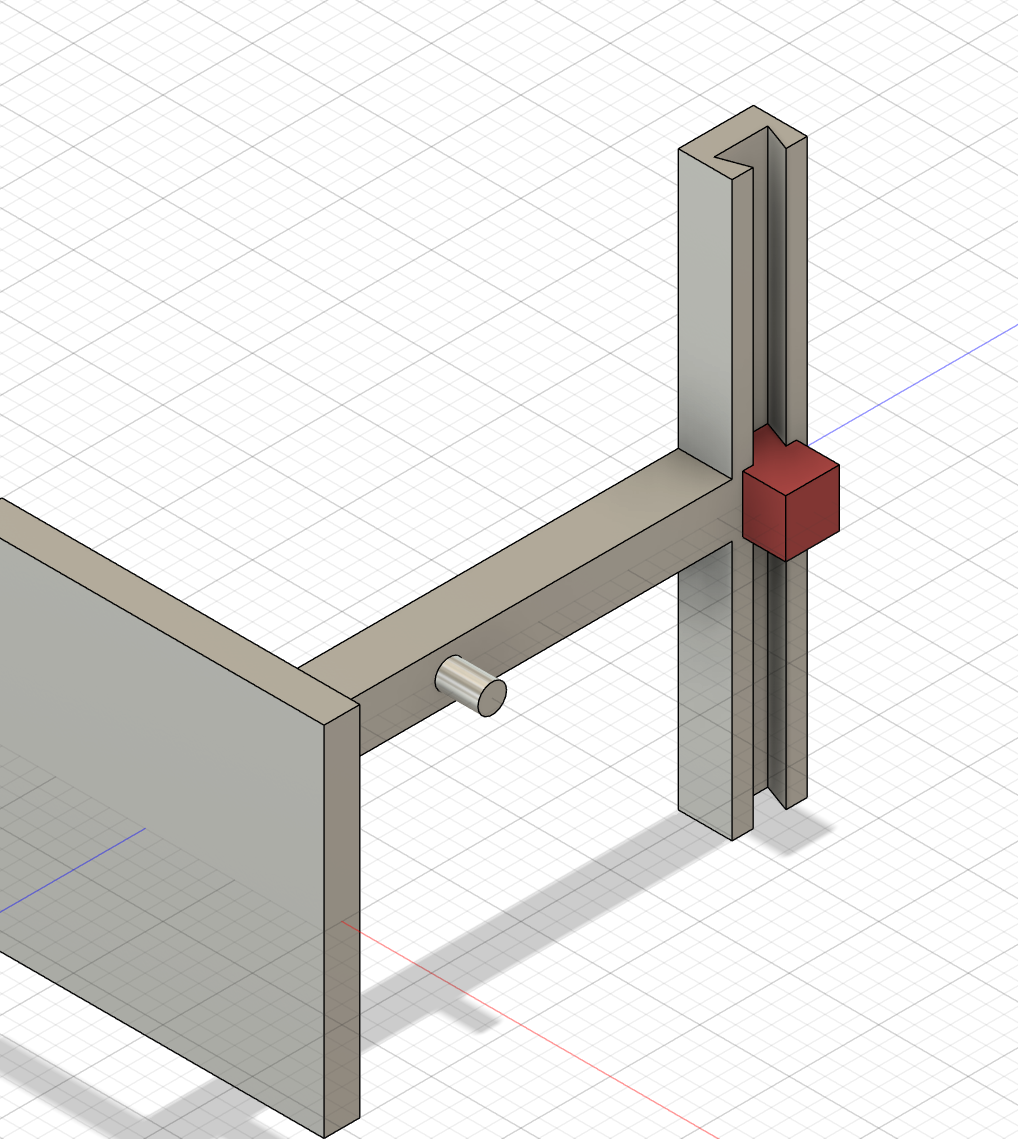
Make a circular turntable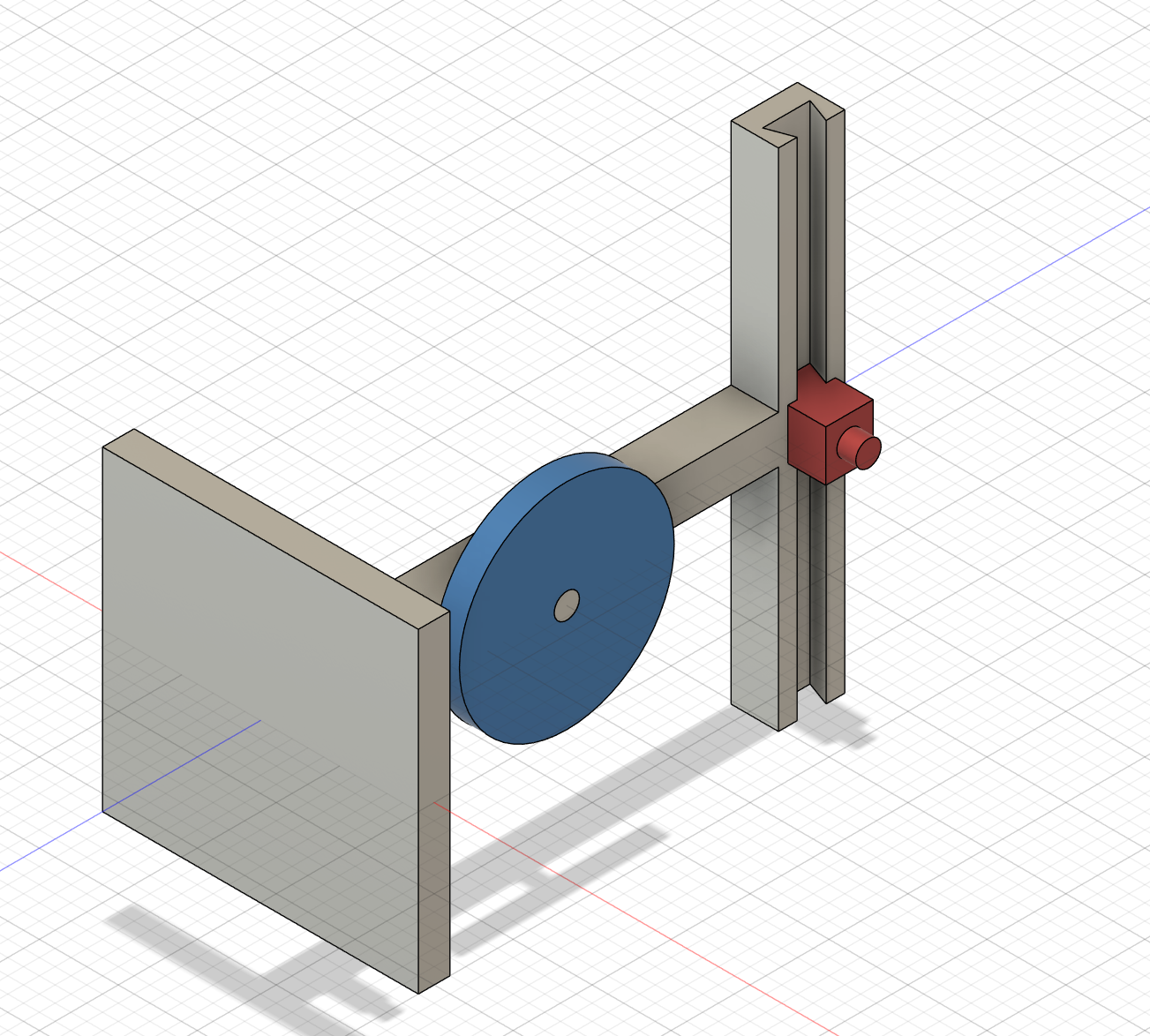
Make the turntable and slider handle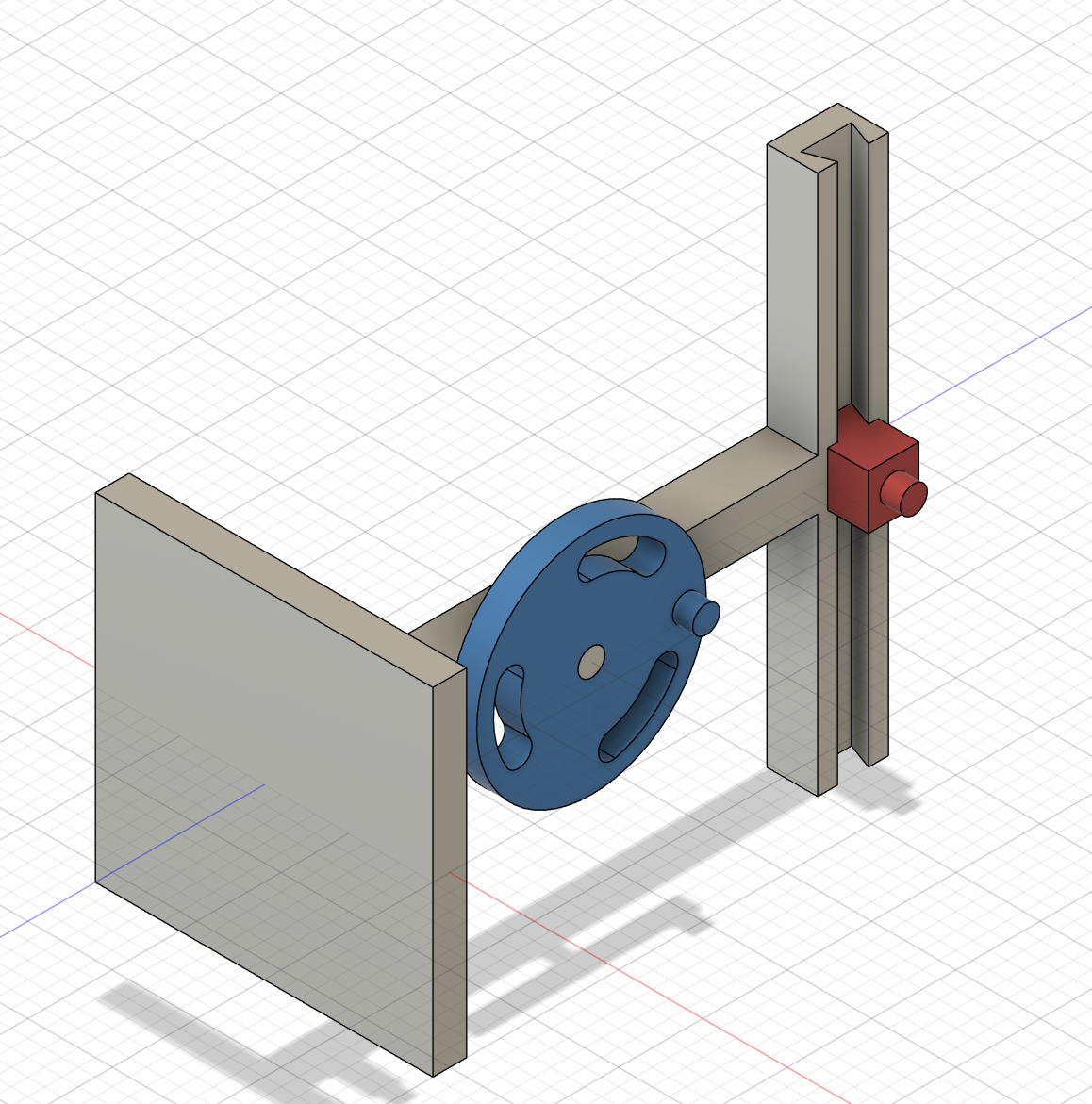
Make the link shaft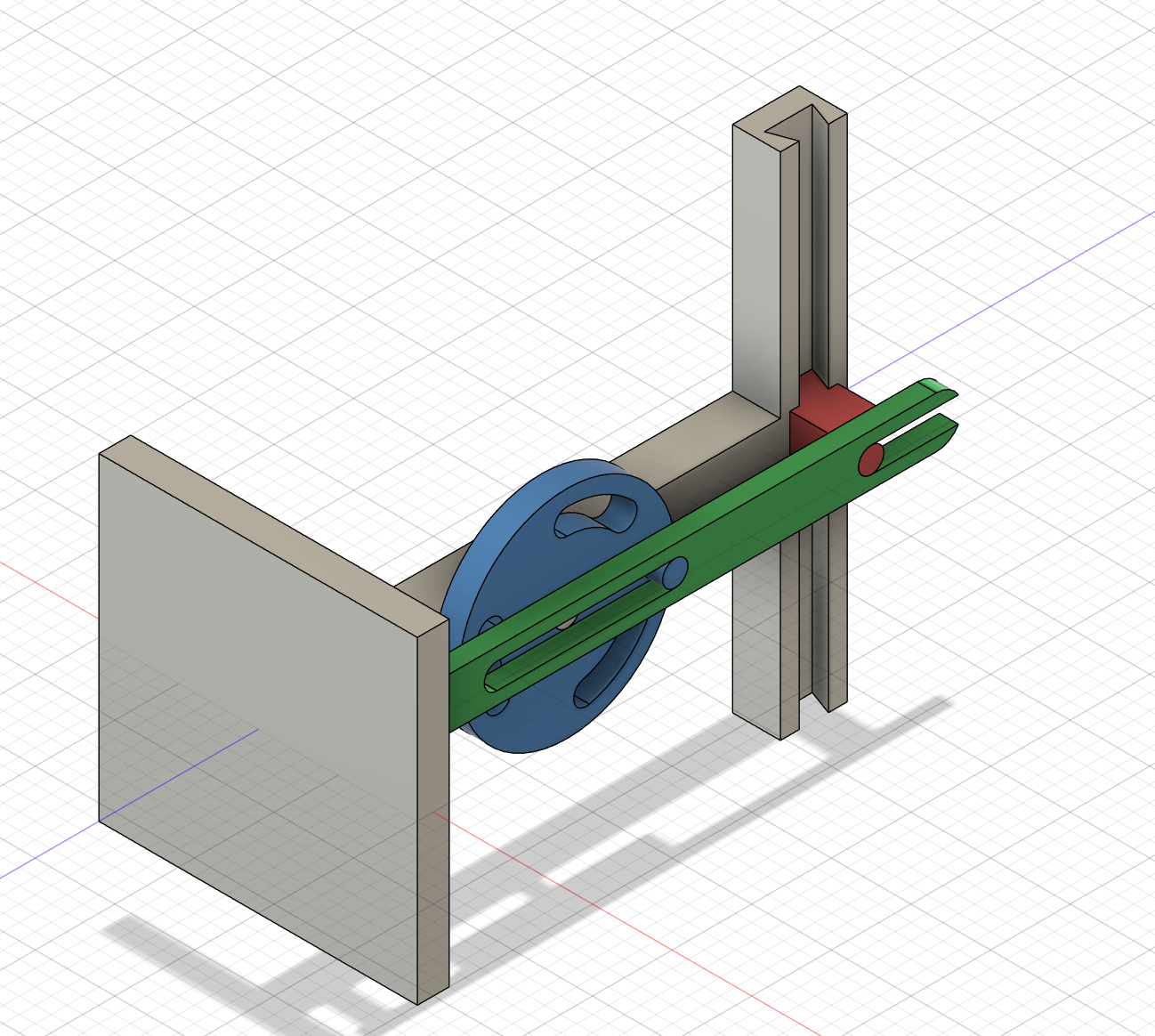
Create link animations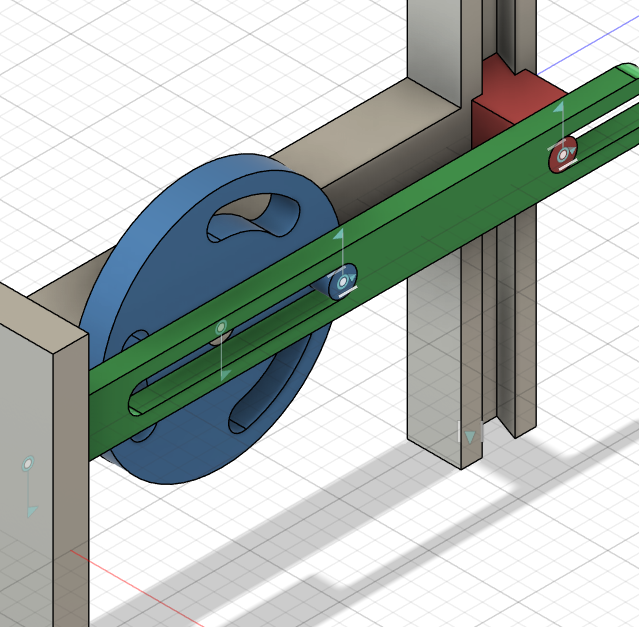

Parameter adjustment 
Engineering drawing 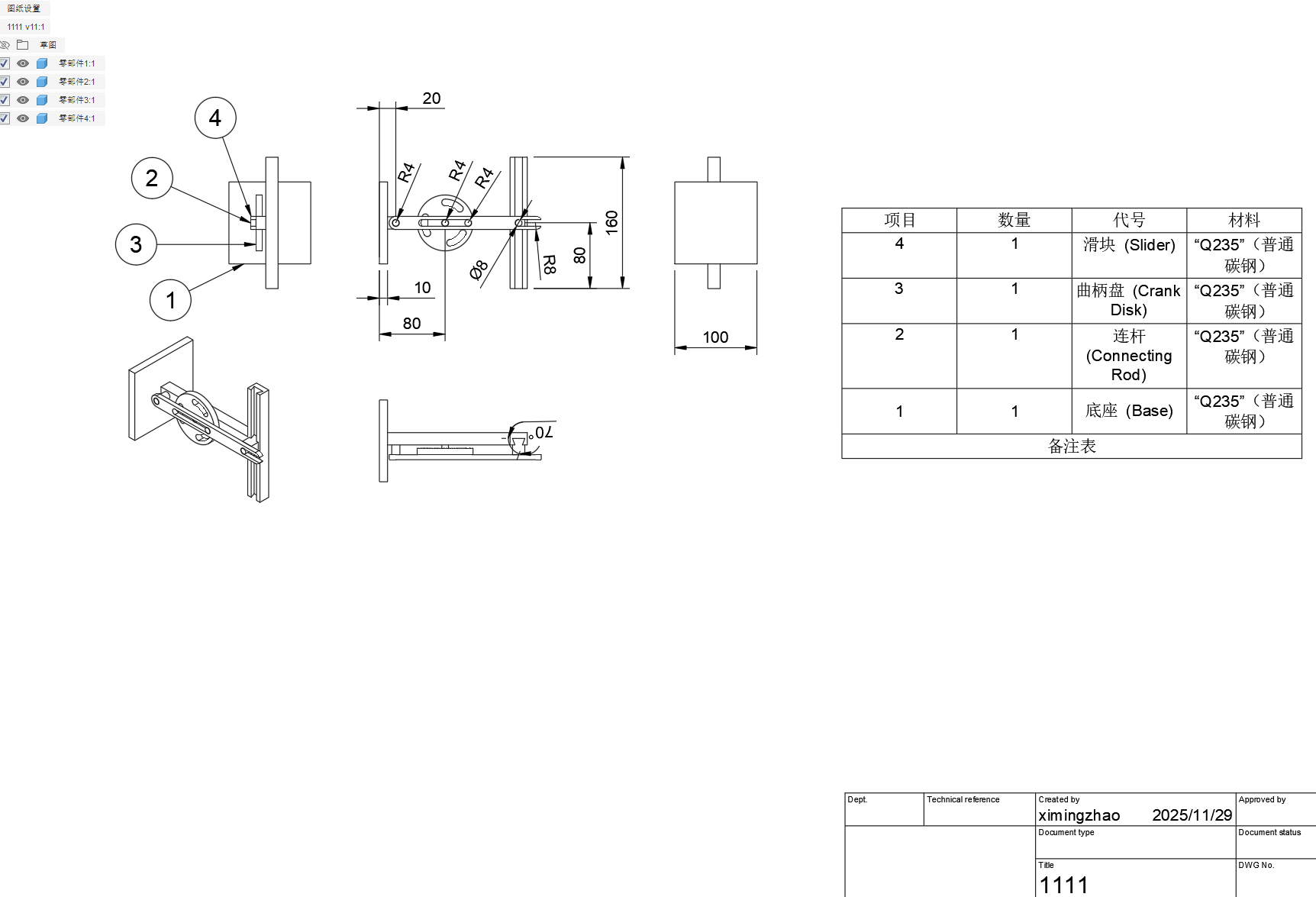
3. Simple introduction to other CAD software
SolidWorks
SolidWorks is a 3D CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software developed by Dassault Systèmes. It is mainly used for mechanical and product design, but is also applied in civil engineering, architecture, and aeronautical design. 
- Powerful 3D modeling features: SolidWorks is known for its intuitive 3D design and product development tools, which can quickly produce high-quality 3D models.
- Simulation and validation: SolidWorks includes a simulation toolkit that allows you to test your product designs before actual manufacturing, helping detect and solve potential problems in advance.
- Non-programming automation: SolidWorks has powerful pattern and configuration tools that let you create similar but slightly different parts, which is useful for rapidly generating product families.
- Electrical and electronic systems design: SolidWorks also offers tools for electrical and electronic system design, which are useful for projects involving complex wiring or electronic components.
- Integrated CAM system: SolidWorks provides integrated CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) tools, so you can plan how to manufacture parts on machine tools while you design the product.
- Wide range of applications: SolidWorks is widely used in fields such as mechanical design, automotive design, electronic devices, medical equipment, industrial equipment, and mold manufacturing.
CATIA
CATIA is a high-end 3D CAD software also developed by Dassault Systèmes. It is widely used in aerospace, automotive, shipbuilding, and other industries that require very complex products and large assemblies. 
- Advanced surface modeling: CATIA is especially strong at complex freeform surfaces, making it suitable for car body, aircraft fuselage, and other aerodynamic shapes.
- Large assembly management: It handles very large and complex assemblies efficiently, which is important for airplanes, cars, and industrial machines.
- Multidisciplinary integration: CATIA supports mechanical design, structural analysis, systems engineering, and even electrical and fluid systems, helping different engineering teams work in a unified platform.
- PLM integration: CATIA is often used together with PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) systems, helping companies manage the whole life of a product from concept to retirement.
- Industry-standard in some fields: In aerospace and automotive industries, CATIA is considered a standard tool and is required by many large companies.
- High learning and application value: Although it is more complex and expensive than entry-level CAD tools, mastering CATIA is very valuable for engineers working in large industrial companies.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is one of the most widely used CAD software products developed by Autodesk, supporting both 2D drafting and basic 3D modeling. 
- Powerful 2D drafting: AutoCAD is especially strong in 2D drawing, commonly used for mechanical drawings, architectural plans, and engineering documentation.
- Broad industry standards: Many industries use DWG/DXF files as standard formats, so AutoCAD drawings are highly compatible and widely accepted.
- Basic 3D capabilities: Although not as specialized in 3D as some other software, AutoCAD still supports 3D modeling for simple solids and surfaces.
- Rich plug-ins and vertical versions: There are many specialized versions (such as AutoCAD Mechanical, AutoCAD Architecture) and third-party plug-ins for different industries.
- Flexible customization: Users can customize commands and workflows using scripts and APIs (such as AutoLISP), improving efficiency.
- Cross-platform support: AutoCAD offers desktop, web, and mobile versions, allowing users to view and edit drawings on different devices.