Molding and Casting: Research & Practice
1. Understanding Processes
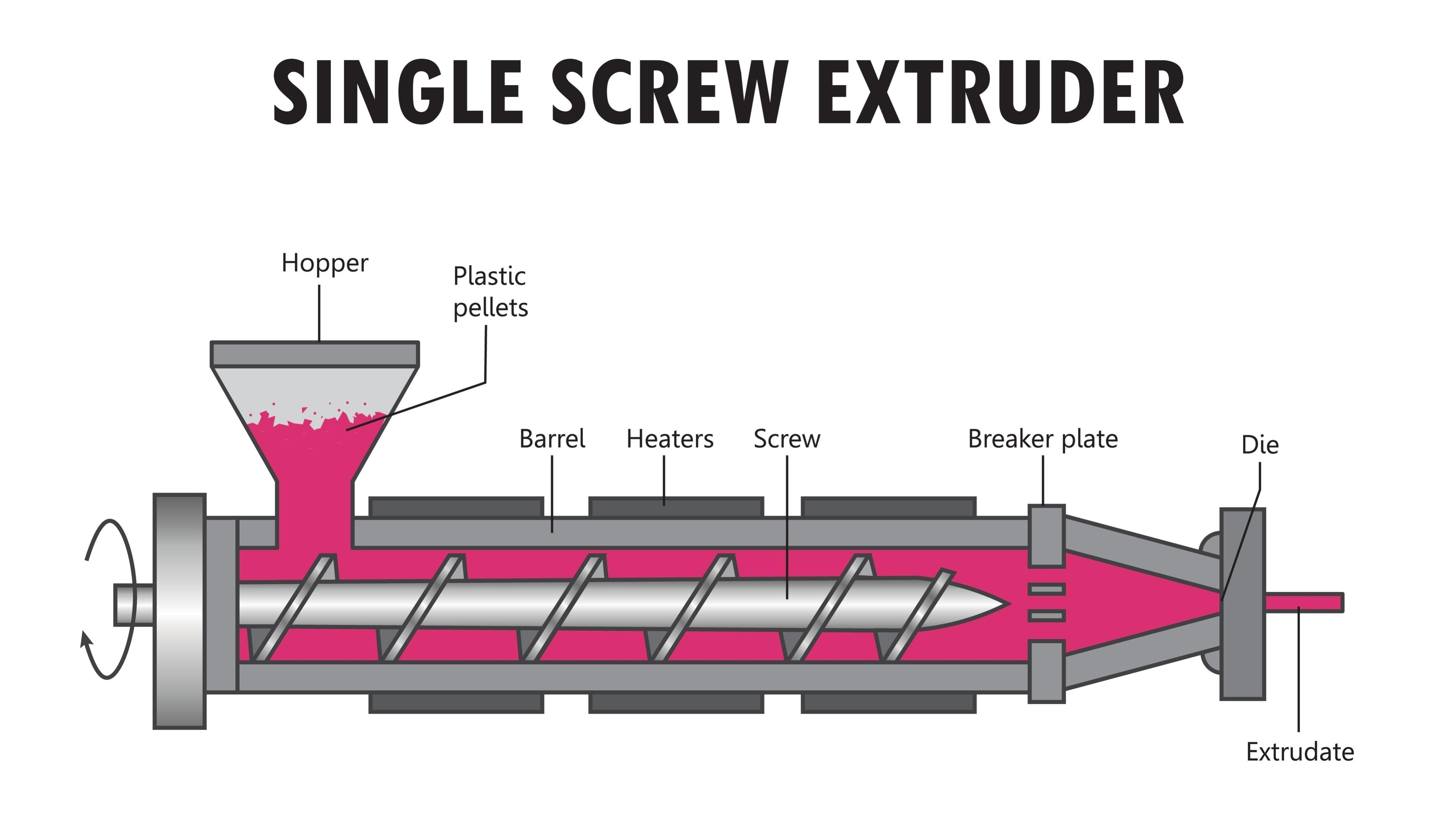
1.1 Existing Process: Injection Molding
Injection Molding is the most standard manufacturing process for producing plastic parts in large volumes.
- Principle: Thermoplastic pellets are melted and injected into a steel mold under high pressure. The material cools and solidifies into the final shape.
- Key Features: High precision, extremely fast cycle times (seconds), and low cost per unit for mass production.
- Limitations: High initial tooling cost (molds are expensive).

1.2 Latest Research: Freeform Injection Molding (FIM)
Freeform Injection Molding (FIM) is a hybrid technology bridging 3D printing and injection molding.
- Innovation: It uses 3D printed soluble resin molds.
- Process:
- Print the mold shell using a specialized dissolvable resin.
- Inject standard thermoplastic into the printed mold.
- Dissolve the mold in a chemical bath, leaving only the complex part.
- Advantages: Allows for complex geometries (undercuts) that are impossible with traditional steel molds. Reduces prototyping lead time from weeks to hours.
2. Materials Study
Material A: Polypropylene (PP)
- Category: Thermoplastic.
- Processing Method: Injection Molding.
- Post-Processing: Gate trimming, flash removal. Surface finish depends on the mold texture.
- Effect: Semi-crystalline, translucent or colored. Extremely flexible, fatigue-resistant (living hinges), and chemically resistant.
- Application: Food containers, automotive bumpers, flip-top bottle caps.

Material B: Polyurethane Resin (PU Resin)
- Category: Thermosetting Polymer.
- Processing Method: Silicone Molding / Vacuum Casting.
- Post-Processing: Sanding parting lines, painting, or plating.
- Effect: Can range from rigid to flexible (rubber-like). Captures extreme surface detail from the silicone mold.
- Application: Prototypes, action figures, small-batch electronic housings.
3. Practical Operation Guide
3.1 Desktop Injection Molding Machine
(Example: Ningbo Taizhu ABS AG15E1-H)
The process of injection molding using ABS material involves several critical steps, including drying the material, setting the proper temperature and pressure, and ensuring accurate injection. Below are the detailed steps and process parameters based on experimentation.
Step-by-Step Process:
Setup and Material Drying:
- Machine: Ningbo Taizhu ABS AG15E1-H.
- Material: ABS.
- Before starting the molding process, it is essential to dry the ABS material to ensure good flow properties during injection.
- Drying Temperature: Set the machine to 85°C.
- Drying Time: Dry the material for 2.5 hours to remove moisture and avoid defects in the final molded parts.
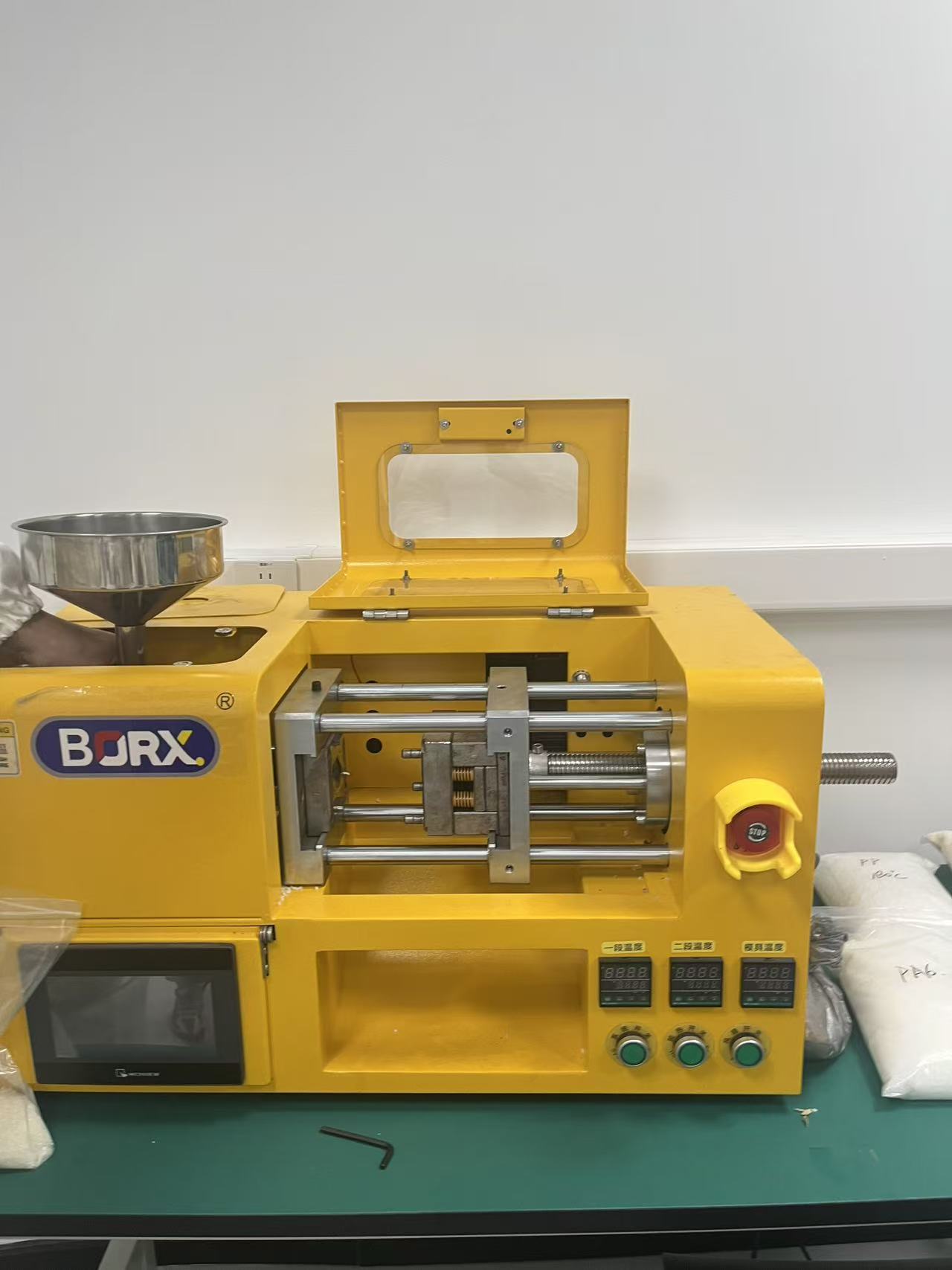

Clamping:
- Place the aluminum mold securely in the machine's mold holder (vise). Ensure the mold is tightly clamped to avoid any excess plastic leakage (flash) during the injection process.
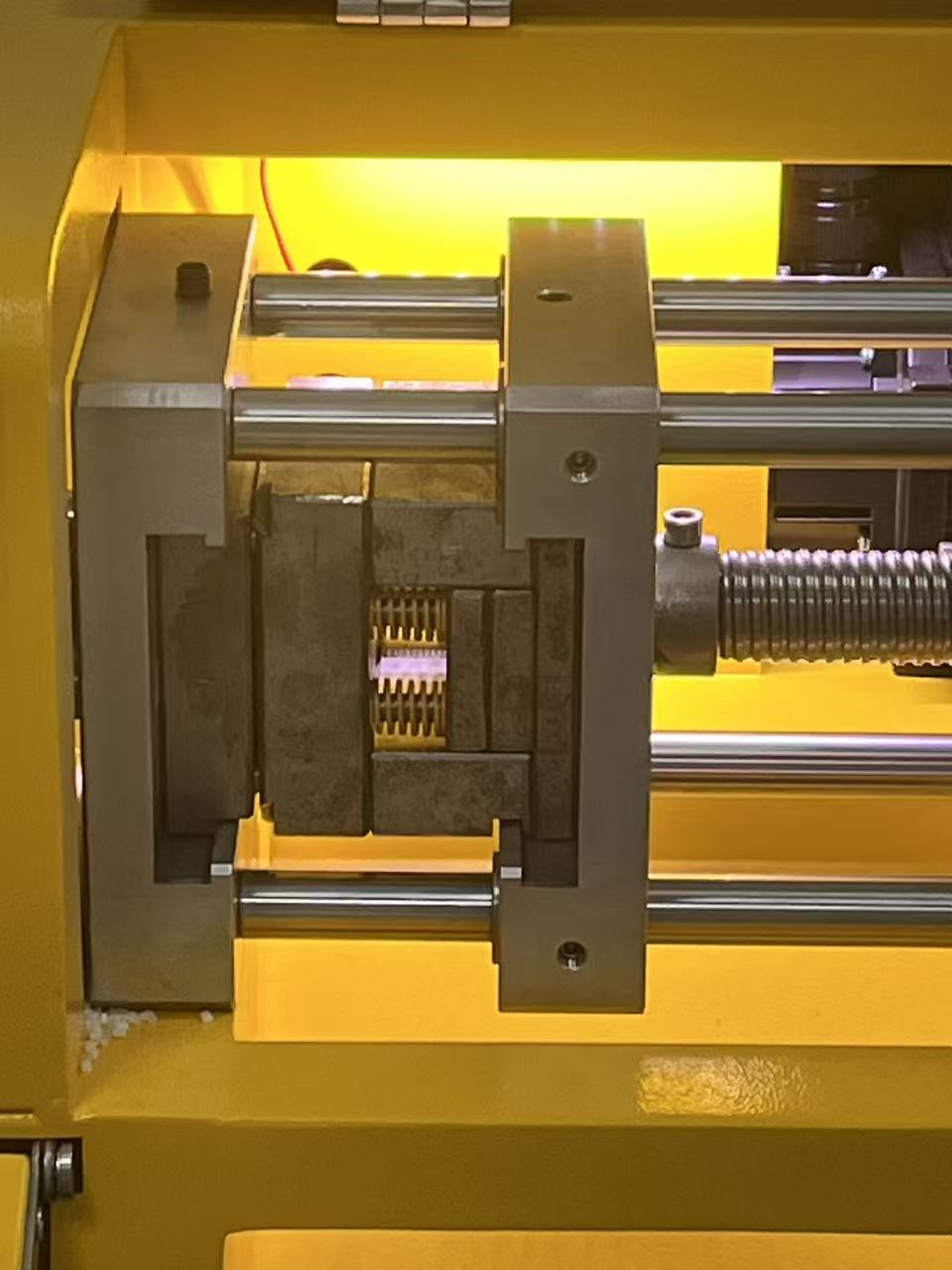
- Place the aluminum mold securely in the machine's mold holder (vise). Ensure the mold is tightly clamped to avoid any excess plastic leakage (flash) during the injection process.
Injection Process:
- First Stage Temperature: 180°C.
- Second Stage Temperature: 220°C.
- Injection Speed:
- First stage: 820.
- Second stage: 815.
- Injection Time: 6.5 seconds.
- The injection speed needs to be carefully adjusted. If the speed is too slow, the molded part may have defects or incomplete shapes. Make sure the machine applies sufficient pressure and the injection speed is suitable to ensure the mold is fully filled. Clamping Process
Cooling:
- After the injection, allow the mold to cool naturally (air cooling). This will help the material solidify and retain its shape before ejection.
- Once cooled, unclamp the mold and eject the finished part.
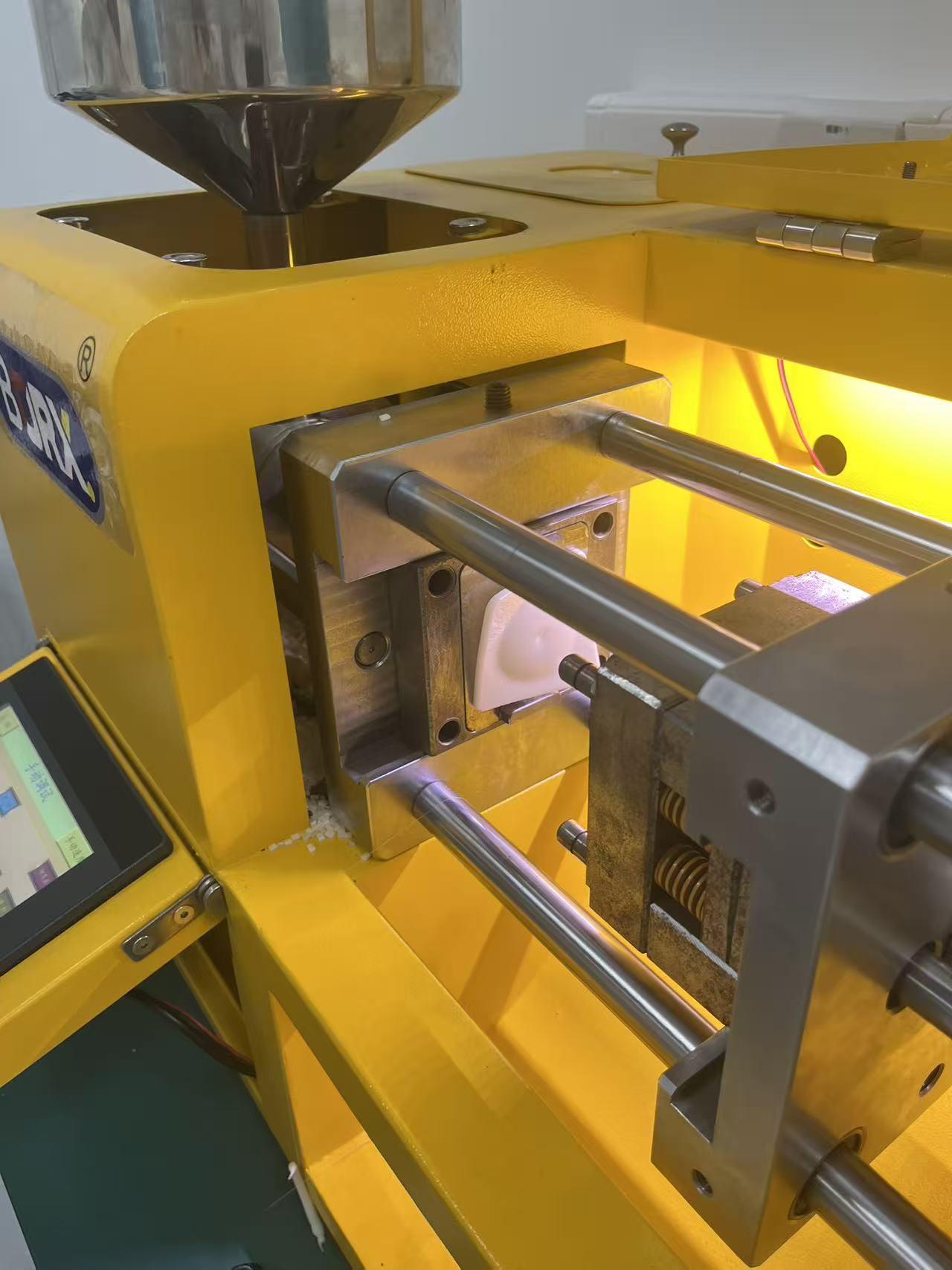

Key Considerations:
Ensure that the machine is tightly clamped throughout the process.
Adjust the injection speed to avoid defects, such as incomplete filling or surface blemishes.
Proper temperature control for both stages is critical for achieving the best molding results.
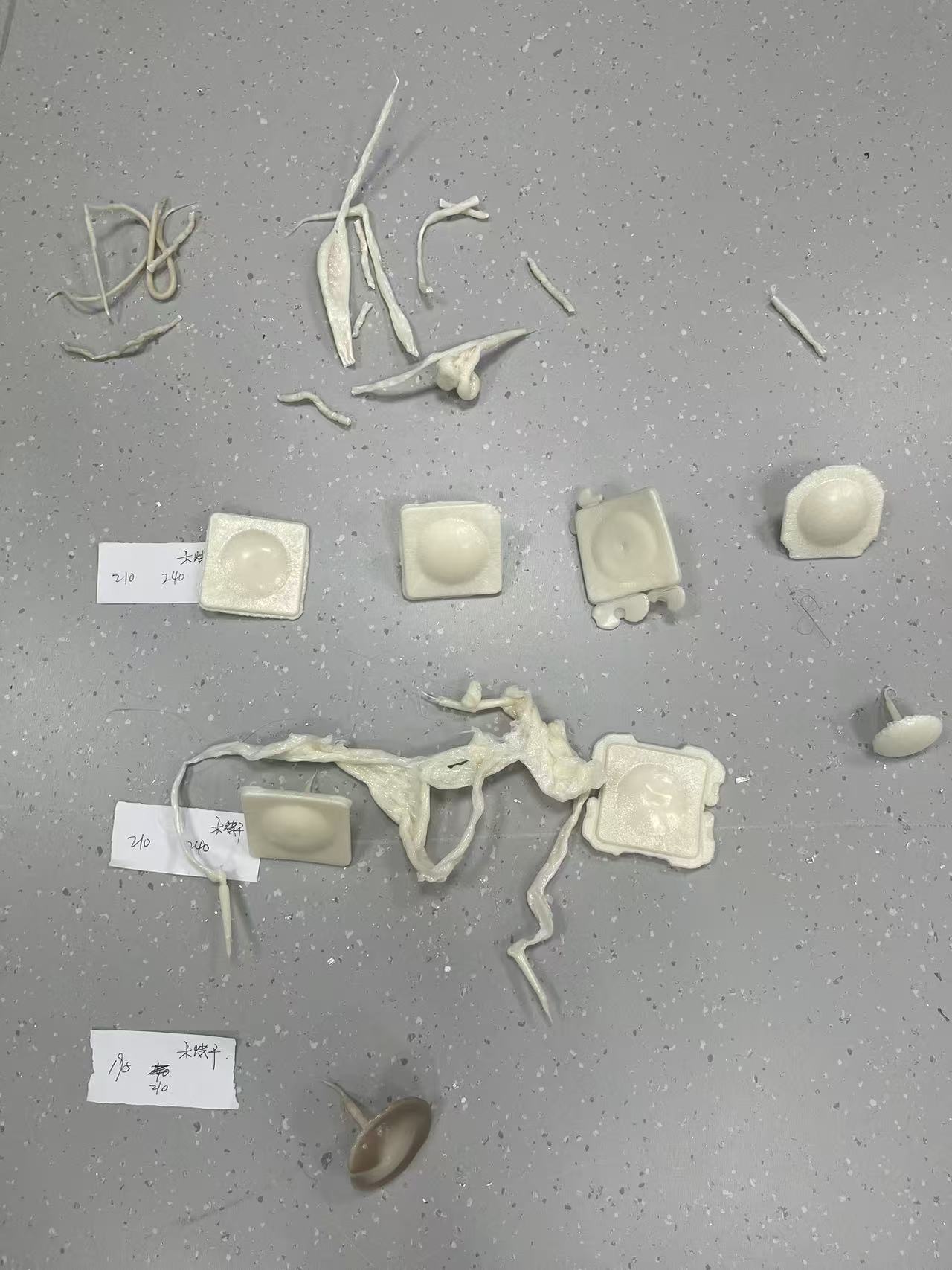

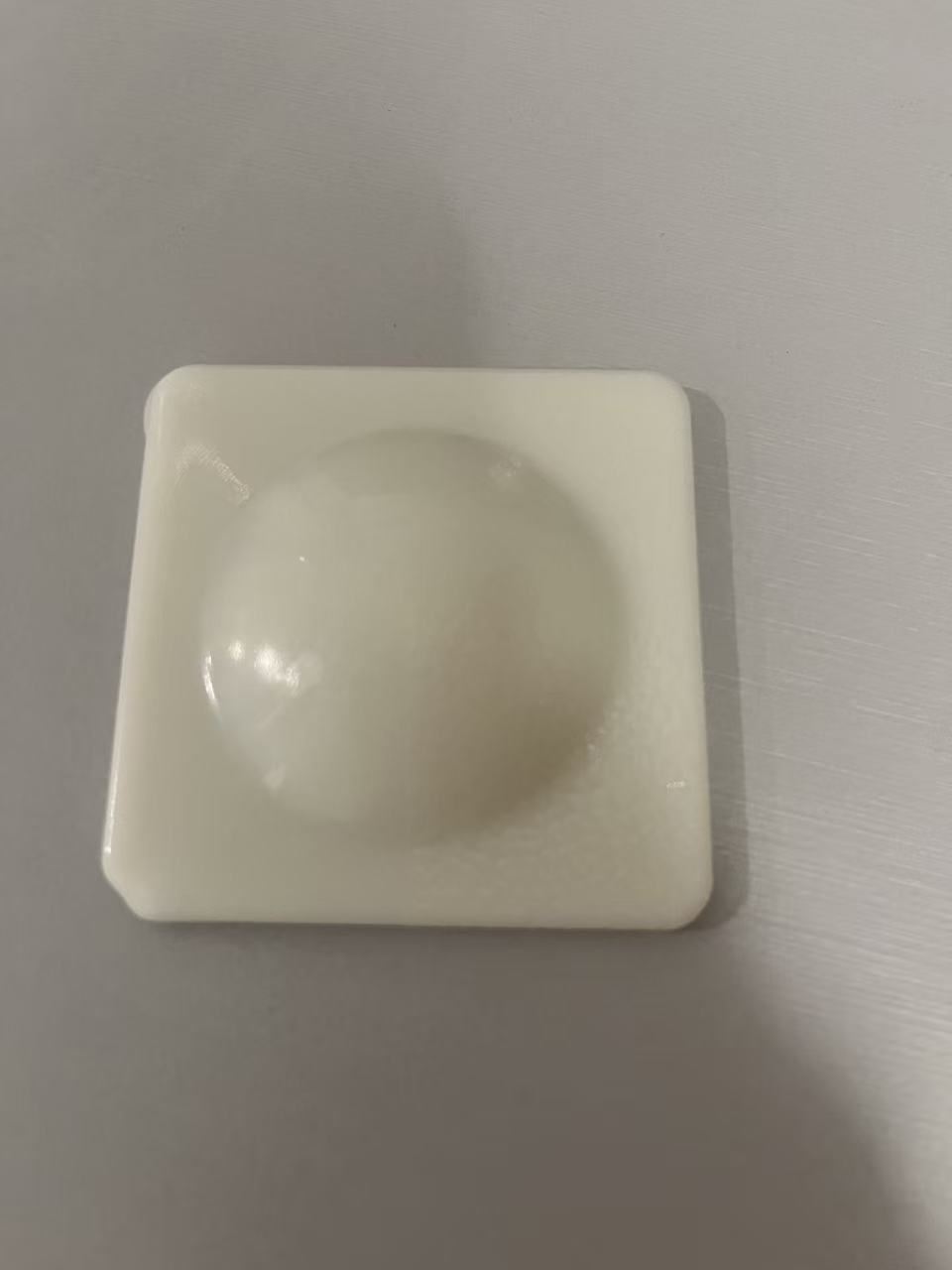
Conclusion:
After experimenting with different settings, the optimal parameters for ABS injection molding on the Ningbo Taizhu ABS AG15E1-H machine are:
- First Stage Temperature: 180°C.
- Second Stage Temperature: 220°C.
- Injection Speed: First stage 820, second stage 815.
- Injection Time: 6.5 seconds.
These settings yield the best results in terms of part quality, with no defects or incomplete shapes.

3.2 Silicone Molding & Casting
- Master Pattern: Secure your master model in a leak-proof mold box (made of LEGOs or acrylic).

- Mixing Silicone: Mix Silicone Part A and Part B by weight (e.g., 1:1 ratio). Stir thoroughly to avoid uncured spots.

Degassing: Place the mixture in a Vacuum Chamber to remove air bubbles. This ensures a smooth mold surface.
Pouring: Pour the silicone from a high point into the lowest corner of the box. Let it flow over the model naturally.
Casting: Once the mold cures, remove the master. Mix your PU Resin and pour it into the silicone mold. Wait for it to cure and demold.
For more details, please visit this link.